4.2 模型量化¶
学习目标:
1.知道什么是量化?
2.能够利用pytorch完成模型量化
1. 什么是模型的量化¶
量化是一种技术,通过使用低精度数据类型(如 8 位整数 (int8))而不是通常的 32 位浮点 (float32))来表示权重和激活,从而降低运行推理的计算和内存成本。减少位数意味着生成的模型需要更少的内存存储,并且使用整数运算可以更快地执行矩阵乘法等运算。它还允许在嵌入式设备或者边缘设备上运行模型,这些设备有时仅支持整数数据类型。将float32量化为int8会实现性能提升:
- 模型尺寸缩小 4 倍;
- 内存带宽减少 2-4 倍;
- 推理速度提高了 2-4 倍(确切的加速取决于硬件、网络和模型等)。
量化背后的基本思想非常简单:从权重和激活的高精度表示(通常是常规的 32 位浮点)到较低精度的数据类型。最常见的低精度数据类型是:
| 数据类型 (Data Type) | 值域 (Range) | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| float16 | ±6.55×10⁴(约±65504) | 半精度浮点数,占用16位,精度低,范围有限。 |
| bfloat16 | ±3.39×10³⁸(近似float32范围) | 脑浮点数,16位,指数范围与float32相同,精度较低。 |
| int16 | -32768 到 32767 | 16位有符号整数,适合整数运算,无小数。 |
| int8 | -128 到 127 | 8位有符号整数,范围小,适合低精度整数运算。 |
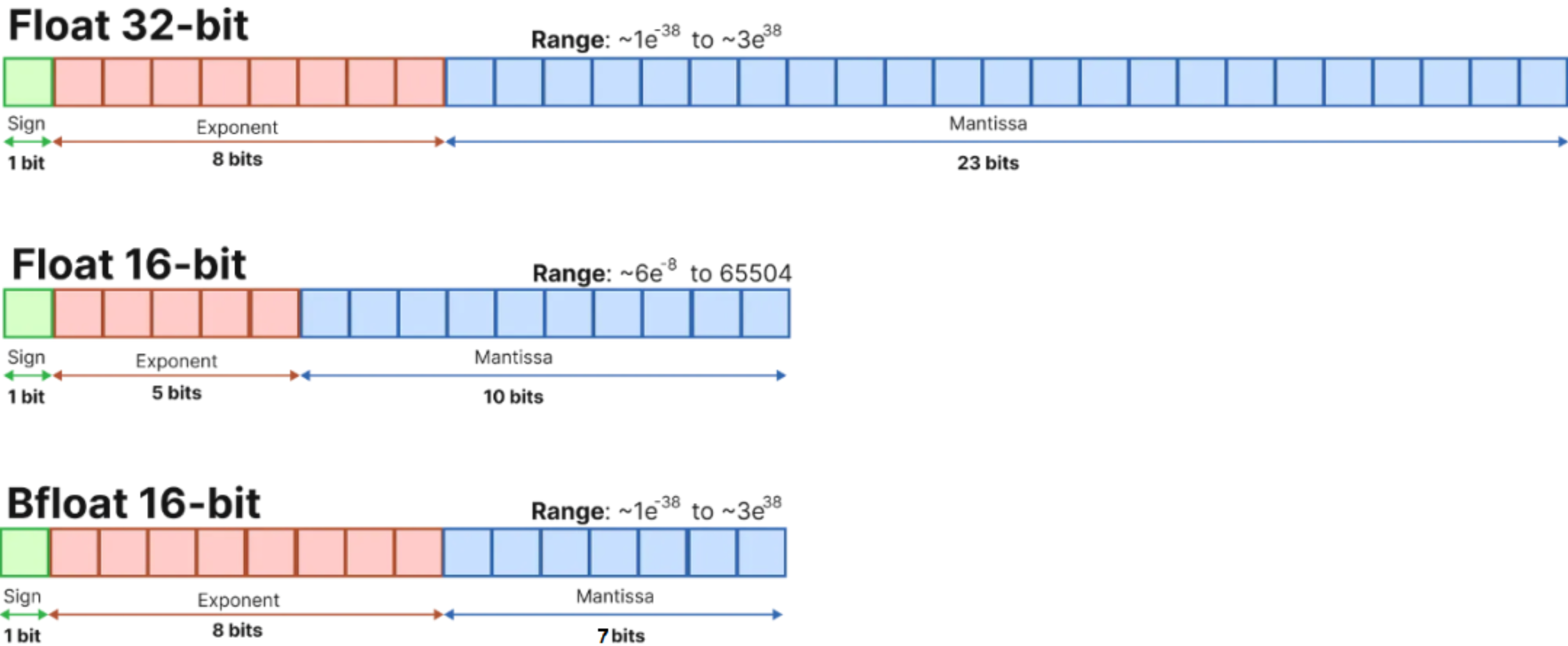
量化:将数据转换为较低精度,如 INT8。量化意味着引入近似值,由此产生的网络精度略低。
2.量化三种方式¶
实际部署的时候需要一些模型加速的方法,每种框架除了fp32精度外,都支持了int8的精度,而量化到int8常常可以使我们的模型更小更快,所以在部署端很受欢迎。常用的模型量化方式有动态量化、训练中量化,QAT,和训练后量化,PTQ。
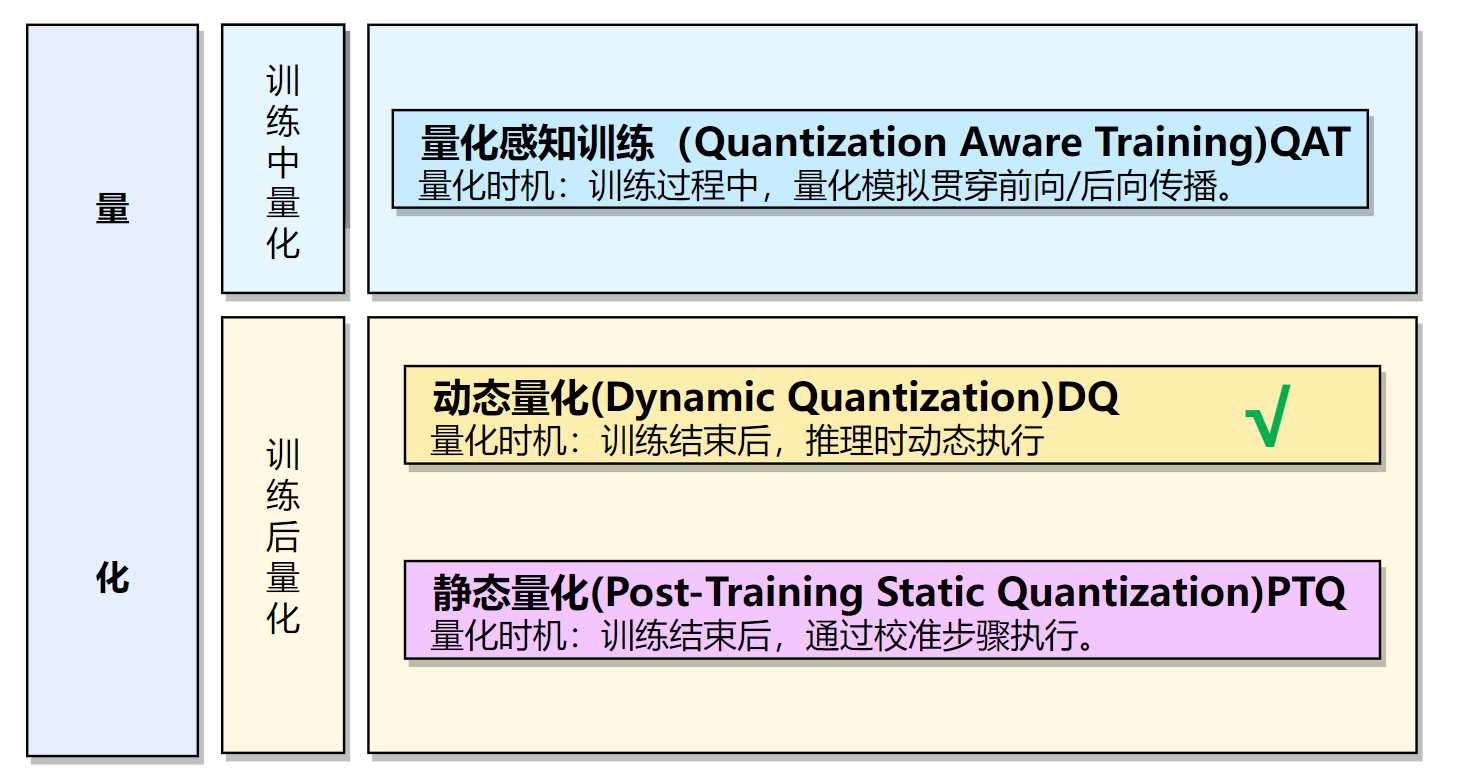
-
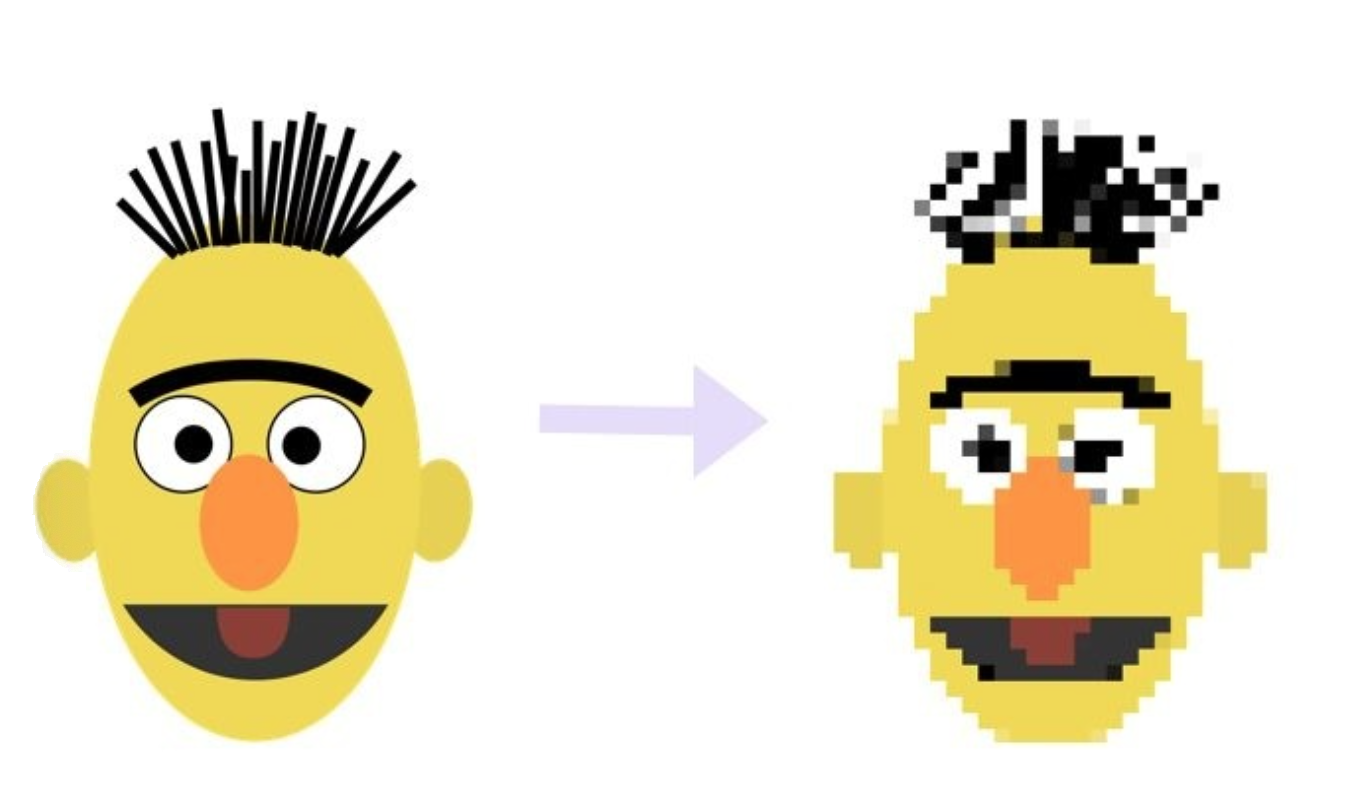
通俗的理解, 就是将模型的参数精度进行降低操作, 用更少的比特位(torch.qint8)代替较多的比特位(torch.float32), 从而缩减模型, 并加速推断速度.
-
如下图所示, 左侧的是原始模型拥有更高的参数精度(float32), 等效于像素高, 看的清晰; 右侧的是量化后的模型, 拥有较低的参数精度(int8), 等效于像素低, 看的模糊, 但依然可以准确的识别图像内容.本次实现训练后的动态量化。

2.Pytorch的量化¶
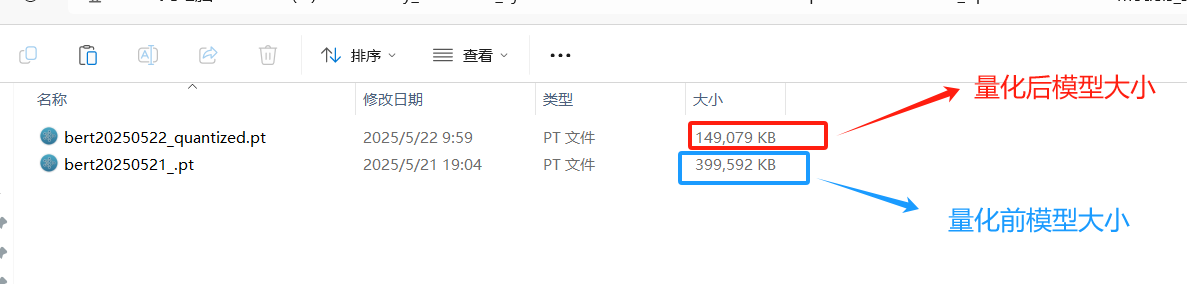
本次直接使用Pytorch的动态量化(Dynamic Quantization),即torch.quantization.quantize_dynamic()来实现量化操作即可,量化需要在cpu中完成,所以需要把设备信息设置为cpu.以下是量化前后的模型大小对比:
3.代码实现¶
代码位置:

核心逻辑:
整个量化代码,核心是增加了bert_model_quantization.py文件以及配置文件微调。
该脚本实现了对已经训练好的 模型进行,通过了torch.quantization.quantize_dynamic()进行了量化。
后续并基于量化得到的模型进行了部署以及推理延时测试。
3.1 配置类文件中的Config类¶
代码位置:
核心增加了量化模型存储路径以及量化device设置为cpu:
import torch
import os
import datetime
from transformers.models import BertModel,BertTokenizer,BertConfig
current_date=datetime.datetime.now().date().strftime("%Y%m%d")
class Config(object):
def __init__(self):
"""
配置类,包含模型和训练所需的各种参数。
"""
self.model_name = "bert" # 模型名称
self.data_path = "../../../01-data" #数据集的根路径
self.train_path = self.data_path + "\\train.txt" # 训练集
self.dev_path = self.data_path + "\\dev3.txt" # 少量验证集,快速验证
self.test_path = self.data_path + "\\test.txt" # 测试集
self.class_path=self.data_path + "\\class.txt" #类别文件
self.class_list = [line.strip() for line in open(self.class_path, encoding="utf-8")] # 类别名单
# 模型训练结果保存路径
self.model_save_path = "../models_save/bert20250521.pt"
# 量化模型保存路径
self.quantized_model_save_path = "../models_save/quantized_model_bertclassifer_model.pt"
# 模型训练+预测的时候
self.device = 'cpu' # 量化时启用
# self.device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") # 训练设备,如果GPU可用,则为cuda,否则为cpu
self.num_classes = len(self.class_list) # 类别数
self.num_epochs = 2 # epoch数
self.batch_size = 2 # mini-batch大小
self.pad_size = 32 # 每句话处理成的长度(短填长切)
self.learning_rate = 5e-5 # 学习率
self.bert_path = "../../../04-bert/bert-base-chinese" # 预训练BERT模型的路径
self.bert_model=BertModel.from_pretrained(self.bert_path)
self.tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(self.bert_path) # BERT模型的分词器
self.bert_config = BertConfig.from_pretrained(self.bert_path) # BERT模型的配置
self.hidden_size = 768 # BERT模型的隐藏层大小
if __name__ == '__main__':
conf = Config()
print(conf.bert_config)
input_size=conf.tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(["你","好","中国","人"])
print(input_size)
print(conf.class_list)
3.2 模型量化实现¶
在这里我们使用3.3节基于bert构建的分类模型进行量化
该部分代码在:
首先导入工具包模块:
from bert_classifer_model import BertClassifier
from config import Config
import numpy as np
import torch
from utils import build_dataloader
from train import model2dev
以下为模型量化的核心逻辑
- 加载数据
- 加载模型
- 模型量化
- 测试量化后的模型
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 1.初始化配置
conf = Config()
# 2.创建数据迭代器
print('加载数据...')
train_dataloader, test_dataloader, dev_dataloader = build_dataloader()
# 3.加载模型
print("加载模型...")
device = conf.device
model = BertClassifier()
model_path = conf.model_save_path
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path, map_location='cpu'))
model.eval()
print("查看量化前的模型结构=========================")
print(model)
# 4.torch.quantization.quantize_dynamic量化BERT模型 dtype=torch.qint8
quantized_model = torch.quantization.quantize_dynamic(model,{torch.nn.Linear},dtype=torch.qint8)
# 检查量化模型中各层的参数数据类型
print("量化后的模型=========================")
print(quantized_model)
# 5.model2dev 测试量化后的模型 (quantized_model, test_dataloader, device)
report, f1score, accuracy, precision = model2dev(quantized_model, test_dataloader, device)
print("Test Classification Report:", report)
print("Test F1:", f1score)
print("Test Accuracy:", accuracy)
print("Test Precision:", precision)
# 6.计算8-bit量化后模型的内存占用(单位:MB)
# sum(p.numel() * p.element_size() for p in quantized_model.parameters()): 遍历模型参数,计算每个参数张量的元素总数(numel)乘以每个元素字节大小(element_size),累加得到总字节数
# / 1024 ** 2: 将字节数转换为兆字节(MB)
# :.2f: 保留两位小数
print(f"8-bit 量化后的模型内存: {sum(p.numel() * p.element_size() for p in quantized_model.parameters()) / 1024 ** 2:.2f} MB")
# 7.保存整个量化模型
torch.save(quantized_model, conf.quantized_model_save_path)
print("保存量化模型成功!地址为:", conf.quantized_model_save_path)
3.3 输出结果¶
模型中的所有Linear层变成了DynamicQuantizedLinear层
加载数据...
Loading data: 180000it [00:00, 1599339.74it/s]
Loading data: 10000it [00:00, 1666125.37it/s]
Loading data: 511it [00:00, 337154.21it/s]
[('中华女子学院:本科层次仅1专业招男生', 3), ('两天价网站背后重重迷雾:做个网站究竟要多少钱', 4), ('东5环海棠公社230-290平2居准现房98折优惠', 1), ('卡佩罗:告诉你德国脚生猛的原因 不希望英德战踢点球', 7), ('82岁老太为学生做饭扫地44年获授港大荣誉院士', 5)]
[('词汇阅读是关键 08年考研暑期英语复习全指南', 3), ('中国人民公安大学2012年硕士研究生目录及书目', 3), ('日本地震:金吉列关注在日学子系列报道', 3), ('名师辅导:2012考研英语虚拟语气三种用法', 3), ('自考经验谈:自考生毕业论文选题技巧', 3)]
[('恒指半日跌45点报19859 成交230亿元', 2), ('三羊资产清盘事起ITAT', 0), ('多重利好于一身住总万科金域华府6月开盘', 1), ('谢晋之子谢衍病逝享年59岁(图)', 9), ('江苏16日填报体艺类公办本科征求志愿', 3)]
加载模型...
查看量化前的模型结构=========================
BertClassifier(
(bert): BertModel(
(embeddings): BertEmbeddings(
(word_embeddings): Embedding(21128, 768, padding_idx=0)
(position_embeddings): Embedding(512, 768)
(token_type_embeddings): Embedding(2, 768)
(LayerNorm): LayerNorm((768,), eps=1e-12, elementwise_affine=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(encoder): BertEncoder(
(layer): ModuleList(
(0-11): 12 x BertLayer(
(attention): BertAttention(
(self): BertSdpaSelfAttention(
(query): Linear(in_features=768, out_features=768, bias=True)
(key): Linear(in_features=768, out_features=768, bias=True)
(value): Linear(in_features=768, out_features=768, bias=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(output): BertSelfOutput(
(dense): Linear(in_features=768, out_features=768, bias=True)
(LayerNorm): LayerNorm((768,), eps=1e-12, elementwise_affine=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
(intermediate): BertIntermediate(
(dense): Linear(in_features=768, out_features=3072, bias=True)
(intermediate_act_fn): GELUActivation()
)
(output): BertOutput(
(dense): Linear(in_features=3072, out_features=768, bias=True)
(LayerNorm): LayerNorm((768,), eps=1e-12, elementwise_affine=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
)
(pooler): BertPooler(
(dense): Linear(in_features=768, out_features=768, bias=True)
(activation): Tanh()
)
)
(fc): Linear(in_features=768, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
量化后的模型=========================
BertClassifier(
(bert): BertModel(
(embeddings): BertEmbeddings(
(word_embeddings): Embedding(21128, 768, padding_idx=0)
(position_embeddings): Embedding(512, 768)
(token_type_embeddings): Embedding(2, 768)
(LayerNorm): LayerNorm((768,), eps=1e-12, elementwise_affine=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(encoder): BertEncoder(
(layer): ModuleList(
(0-11): 12 x BertLayer(
(attention): BertAttention(
(self): BertSdpaSelfAttention(
(query): DynamicQuantizedLinear(in_features=768, out_features=768, dtype=torch.qint8, qscheme=torch.per_tensor_affine)
(key): DynamicQuantizedLinear(in_features=768, out_features=768, dtype=torch.qint8, qscheme=torch.per_tensor_affine)
(value): DynamicQuantizedLinear(in_features=768, out_features=768, dtype=torch.qint8, qscheme=torch.per_tensor_affine)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(output): BertSelfOutput(
(dense): DynamicQuantizedLinear(in_features=768, out_features=768, dtype=torch.qint8, qscheme=torch.per_tensor_affine)
(LayerNorm): LayerNorm((768,), eps=1e-12, elementwise_affine=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
(intermediate): BertIntermediate(
(dense): DynamicQuantizedLinear(in_features=768, out_features=3072, dtype=torch.qint8, qscheme=torch.per_tensor_affine)
(intermediate_act_fn): GELUActivation()
)
(output): BertOutput(
(dense): DynamicQuantizedLinear(in_features=3072, out_features=768, dtype=torch.qint8, qscheme=torch.per_tensor_affine)
(LayerNorm): LayerNorm((768,), eps=1e-12, elementwise_affine=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
)
)
(pooler): BertPooler(
(dense): DynamicQuantizedLinear(in_features=768, out_features=768, dtype=torch.qint8, qscheme=torch.per_tensor_affine)
(activation): Tanh()
)
)
(fc): DynamicQuantizedLinear(in_features=768, out_features=10, dtype=torch.qint8, qscheme=torch.per_tensor_affine)
)
Bert Classifier Evaluating ......: 100%|██████████| 40/40 [00:54<00:00, 1.37s/it]
Test Classification Report: precision recall f1-score support
0 0.95 0.82 0.88 1000
1 0.93 0.92 0.93 1000
2 0.80 0.85 0.82 1000
3 0.96 0.93 0.95 1000
4 0.71 0.92 0.80 1000
5 0.94 0.85 0.89 1000
6 0.93 0.85 0.89 1000
7 0.96 0.96 0.96 1000
8 0.95 0.91 0.93 1000
9 0.88 0.93 0.90 1000
accuracy 0.89 10000
macro avg 0.90 0.89 0.89 10000
weighted avg 0.90 0.89 0.89 10000
Test F1: 0.8926
Test Accuracy: 0.8926
Test Precision: 0.8926
8-bit 量化后的模型内存: 63.55 MB
保存量化模型成功!地址为: ../models_save/quantized_model_bertclassifer_model.pt
预测日志:
结论:
模型参数文件大小缩减了62.8%左右(390M-->145M), 相较于原BERT模型,推理时间提升82.4%左右,同时考虑到F1值仅仅下降了4个多百分点, 效果非常优异!
4.本节小结¶
- 实现了对模型的动态量化, 并在CPU上测试了量化后的模型的表现, 验证了BERT模型具有良好的鲁棒性.
-
对比了BERT模型量化前后的大小, 说明BERT模型的压缩率很高, 同时还能保持表现不会显著下降.
-
注意: 如果将模型加载到GPU上直接量化, 会报错如下: